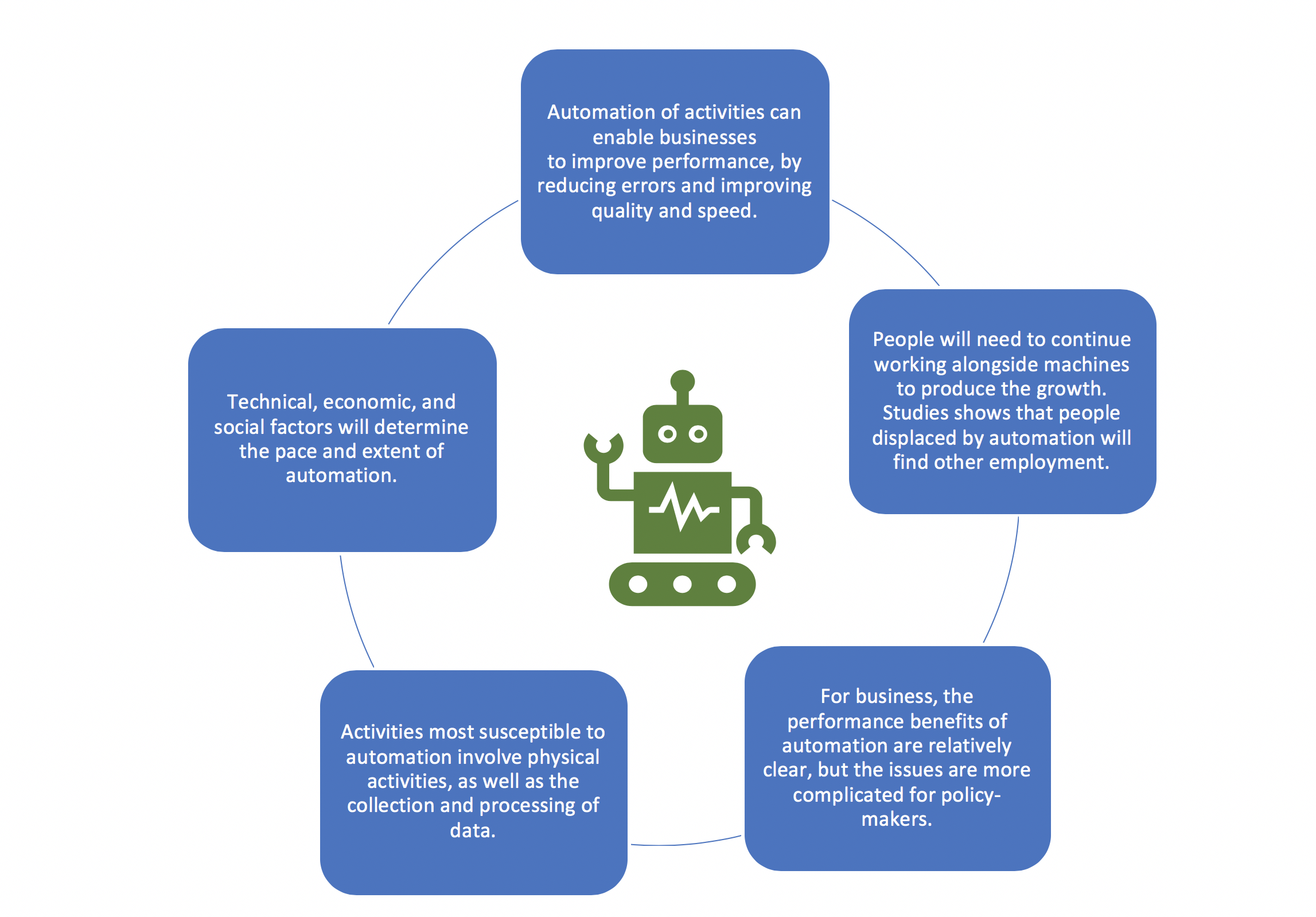
The impact of AI on the labor market has become an inescapable topic of discussion, as it fundamentally transforms the way we work and interact with technology. Recent studies highlight the profound effects of artificial intelligence labor market dynamics, revealing patterns of job displacement due to AI that could redefine entire industries. Economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers have explored these changes, analyzing over a century of data to illustrate how occupational churn is influenced by emerging AI technology effects. As AI continues to evolve, it raises important questions about the future of work with AI in various sectors, especially in terms of skill requirements and job availability. Understanding these shifts is crucial for both workers and employers navigating this new employment landscape.
The influence of advanced technology on employment trends has prompted fresh analysis of labor market dynamics. As automation capabilities broaden, the conversation around the repercussions for various job sectors intensifies, particularly regarding the potential for job loss and the restructuring of roles across industries. Recent findings suggest that innovations in intelligent systems are not only reshaping existing positions but are also paving the way for new opportunities that demand a higher skill set. This occupational transformation points towards a need for continuous adaptation, as labor markets brace for the inevitable shifts sparked by the rise of intelligent machines. The dialogue around this subject encompasses broader themes of workforce evolution and the necessity for strategic workforce development initiatives.
The Transformational Role of AI in the Labor Market
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is making profound changes to the labor market, marking a new era reminiscent of past technological disruptions. Economists like David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers highlight that the current wave of AI adoption mirrors historical shifts brought by tools like electricity and the computer. Their research indicates that AI technology is not merely a temporary trend but a pivotal force reshaping jobs and industries, leading to significant occupational churn analysis. As firms increasingly invest in AI capabilities, the demand for high-skilled labor is surging, suggesting a shift toward a more tech-driven workforce.
The implications of AI on job displacement due to technology are considerable. While fears of widespread job loss are prevalent, the data shows a more complex picture. Many low-paying jobs are witnessing a decline, while demand for more skilled positions is on the rise, causing a transformation in the types of jobs available. This shift could potentially lead to a future of work with AI where roles that require advanced technology skills dominate, highlighting the importance of reskilling and upskilling for the current workforce.
Understanding Occupational Churn in the Age of AI
Occupational churn, which reflects the volatility of job sectors, has been particularly pronounced with the advent of AI technologies. Deming and Summers’ study reveals two distinct phases in the labor market; a period of stability followed by rapid changes driven by technological disruption. The findings show that job polarization, once a concern, appears to be decreasing as new opportunities emerge for skilled workers. As AI continues to evolve, it significantly affects the composition of jobs, leading to an increase in higher-paid roles that require advanced training and technical skills.
The historical lens on occupational churn analysis provides a valuable framework for understanding current labor market dynamics. The researchers note that while the rise of AI technologies has resulted in concerning trends, such as job loss in certain sectors, it also opens doors to new opportunities. The rapid adoption of AI in various industries signals not only an adjustment in the workforce but also a drive towards a better-prepared workforce capable of adapting to future technological advancements.
Trends in Job Growth and the Rise of STEM Fields
As AI technology advances, it significantly contributes to the growth of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) jobs, which are increasingly becoming critical in the modern economy. The research indicates that between 2010 and 2024, the share of STEM jobs has surged nearly 50%, emphasizing the transition towards a workforce that demands higher technological proficiency. This rapid growth reflects a broader trend influenced by AI technology effects, as companies seek individuals equipped to harness and leverage these advanced tools effectively.
The increase in STEM job opportunities illustrates the dual challenges and prospects presented by AI. While certain lower-paid jobs are declining, the demand for skilled professionals is growing, creating a shift in job concentration. This emerging phenomenon highlights the need for educational reforms and initiatives to ensure that the workforce is prepared to meet the demands of an AI-driven job market. As automation continues to shape job availability, emphasis on educational pathways that encourage technological literacy is crucial.
AI and the Evolving Nature of Work
The integration of AI into the labor market is redefining work in multiple sectors, affecting how individuals perform their tasks and the types of roles available. AI’s impact can potentially lead to enhanced productivity for knowledge workers, as firms are expected to leverage the capabilities of these technologies to drive efficiency. Lawrence H. Summers has pointed out that every professional should consider how AI may change their work processes, suggesting a paradigm shift where technology becomes integral to daily functions.
As the future of work with AI unfolds, employers and employees alike must adapt to these changes. The transition into more AI-responsive roles can empower workers with innovative tools that improve productivity but may also lead to the obsolescence of certain job functions. This clearly indicates a pressing need for continuous learning and adaptation within the workforce to stay relevant in a rapidly transforming job landscape influenced by AI.
Investment Trends in AI and Future Employment
Investment in AI technologies is reshaping the employment landscape by creating new roles while rendering others obsolete. Recent findings suggest that companies are increasingly prioritizing investment in AI at record levels, leading to significant changes in the distribution of jobs across the economy. As firms look to harness AI to streamline processes, this drive towards automation results in enhanced operational efficiency but also raises concerns about job displacement in lower-skilled sectors. The employment share in many traditional roles is dropping while the demand for skilled labor rises substantially.
The growing trend of investment in AI highlights a significant shift in employment strategies. Companies are not just looking for workers; they are seeking talent that can effectively engage with AI systems and utilize these technologies to their advantage. This change prompts a vital conversation about the upskilling and reskilling need for workers to remain relevant in industries that are quickly adopting AI technologies. Knowledge workers, in particular, must prepare for a landscape where expectations are higher and technological literacy is paramount.
Navigating Job Loss Amid Automation
Job displacement due to AI is a pressing concern for many workers, particularly in lower-paid service sectors where the impact of automation has been felt the strongest. Research indicates that employment in these areas, which saw a massive growth over the previous decades, has dramatically decreased since 2019. Factors contributing to this trend, including the influence of AI, higher wages, and post-pandemic adjustments, suggest that many of these lower-paid roles may not return as businesses adapt to systems that prioritize efficiency and automation.
As industries transform due to AI, those whose work is centered on routine tasks may find themselves at a higher risk of displacement. The pandemic accelerated changes that would have likely occurred regardless; shopping habits shifted online, and many traditional roles became redundant. This shift necessitates a robust response from policymakers and educational institutions to ensure that workers have access to training and resources that allow them to transition into more sustainable job roles as automation continues to reshape the labor market.
AI: Driving Forces Behind Economic Change
The transformative role of AI extends beyond individual job markets to influence broader economic change. Economists are beginning to consider how AI could serve as a pivotal driver of technological evolution, much like electricity or the internet in previous decades. AI’s potential to streamline processes and cut costs presents businesses with new opportunities for growth, but it also contributes to the concept of job displacement due to technology—a concern shared by many workers facing an uncertain future.
Understanding the economic implications of widespread AI adoption is key to preparing for the long-term effects on the labor market. As organizations integrate AI systems, they must also consider the human element of their workforce and the necessary adaptations required. This balancing act between embracing technological advancements and protecting the workforce will shape the trajectory of economic development in the era of AI, dictating how industries evolve and what workers can expect moving forward.
The Call for Reskilling in the Age of AI
As AI technologies continue to permeate the workplace, the call for reskilling and upskilling the current workforce is more pronounced than ever. With the overwhelming evidence that AI may lead to job displacement, employers and employees must prioritize education and training to remain competitive. Investing in reskilling initiatives can help bridge the gap between traditional job functions and the new requirements of a technology-driven economy, ensuring that workers are well-equipped to handle the demands of emerging roles.
Furthermore, as AI technology effects become more evident, there is an increasing realization that the labor market will require adaptability. Continuous learning will transform from a nice-to-have to a necessity, where workers will need to embrace new skills related to AI and technology to secure their positions. Policymakers, businesses, and educational systems must collaborate to create accessible pathways for workers to gain the skills needed to thrive in a future shaped by AI.
AI’s Influence on Work Culture and Collaboration
AI’s transformative effects are not limited to job roles alone; they are also reshaping work culture and collaboration methods across industries. The integration of AI technologies into everyday tasks can enhance communication, streamline workflows, and facilitate more efficient collaboration among team members. This cultural shift requires a mindset change where employees embrace AI as a tool that can augment their capabilities while also necessitating new forms of teamwork and interaction.
As AI continues to evolve, organizations must prioritize fostering a culture that embraces innovation and technological integration. This includes open communication about AI’s role within the workplace, encouraging workers to leverage these tools without fear of obsolescence. Building a collaborative environment that values the synergy between human intelligence and AI will be crucial for navigating the complex landscape of the future of work, ensuring that technology serves as a partner in productivity and creativity.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting the labor market today?
Artificial intelligence is already reshaping the labor market by influencing job creation and displacement. Recent studies indicate a significant increase in high-skilled job opportunities, especially in STEM fields, driven by AI technology. At the same time, lower-skilled and routine jobs, such as retail sales positions and low-paid service work, are seeing substantial declines, suggesting that job displacement due to AI is a real concern.
What evidence is there of job displacement due to AI in the current workforce?
Evidence from a study on the U.S. labor market over the past century indicates that AI is driving significant occupational churn. While job polarization previously characterized the market, recent trends show a growth in high-compensated roles, particularly in science and technology sectors, alongside a decline in jobs that require lower skills. This indicates potential job displacement due to AI for numerous traditional roles.
What trends are associated with AI technology effects in the labor market?
Recent research identifies several key trends due to AI technology effects, including: 1) An increase in high-skilled job opportunities, particularly in STEM fields. 2) A significant decline in low-paid service and retail jobs. 3) An overall shift towards roles that demand greater technical proficiency and training. These trends suggest a profound transformation in the labor market as AI continues to evolve.
What does occupational churn analysis reveal about the future of work with AI?
Occupational churn analysis reveals that the future of work with AI may lead to higher employment volatility, particularly for low-skilled jobs facing automation. While there are increases in high-skilled positions, the overall job landscape is changing rapidly, as indicated by the significant decline in certain sectors, like retail. This dynamic suggests that workers may need to adapt continuously to the evolving job market driven by AI.
Will AI lead to the creation or loss of jobs in the coming years?
The impact of AI on the future labor market is expected to be complex, with both job creation and loss occurring simultaneously. While advancements in AI are likely to create new opportunities in technology and skilled sectors, they will also result in job loss in traditional roles that automation can replace. Thus, understanding AI’s dual role in the labor market is crucial for future workforce strategies.
What are the long-term implications of AI on job security?
Long-term implications of AI on job security include increased demands for higher skills and immediate adaptability among workers. As organizations integrate AI into their workflows, workers may face pressures to perform tasks more efficiently and with shorter deadlines. This shift could lead to greater instability in job security for roles that rely on traditional methods rather than leveraging AI capabilities.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Polarization | The labor market growth is now favoring well-compensated employees with high levels of training and skills, reversing prior trends of job polarization which saw a growth in low-paid jobs without a corresponding growth in middle/high-paid jobs. |
| STEM Job Increase | The share of STEM jobs has surged from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024, driven by increasing investment in technical talent and technologies, including AI. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Jobs | There is a flat or declining trend in low-paid service jobs since 2019, potentially influenced by AI, wage increases, and lasting pandemic effects. |
| Retail Job Reduction | Retail sales jobs dropped from 7.5% to 5.7% from 2013 to 2023, significantly impacted by e-commerce and AI’s predictive capabilities, particularly during the pandemic. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident as technological advancements drive significant changes in job distribution and employment patterns. Research highlights a shift towards higher-skilled, better-paying jobs while simultaneously indicating a decline in traditional low-paid positions, especially in retail and services. As AI continues to reshape industries, the labor market will face both opportunities for innovation and challenges related to job displacement. Overall, the evolution prompted by AI suggests a need for workers to adapt to new roles and skills that align with the changing landscape of work.